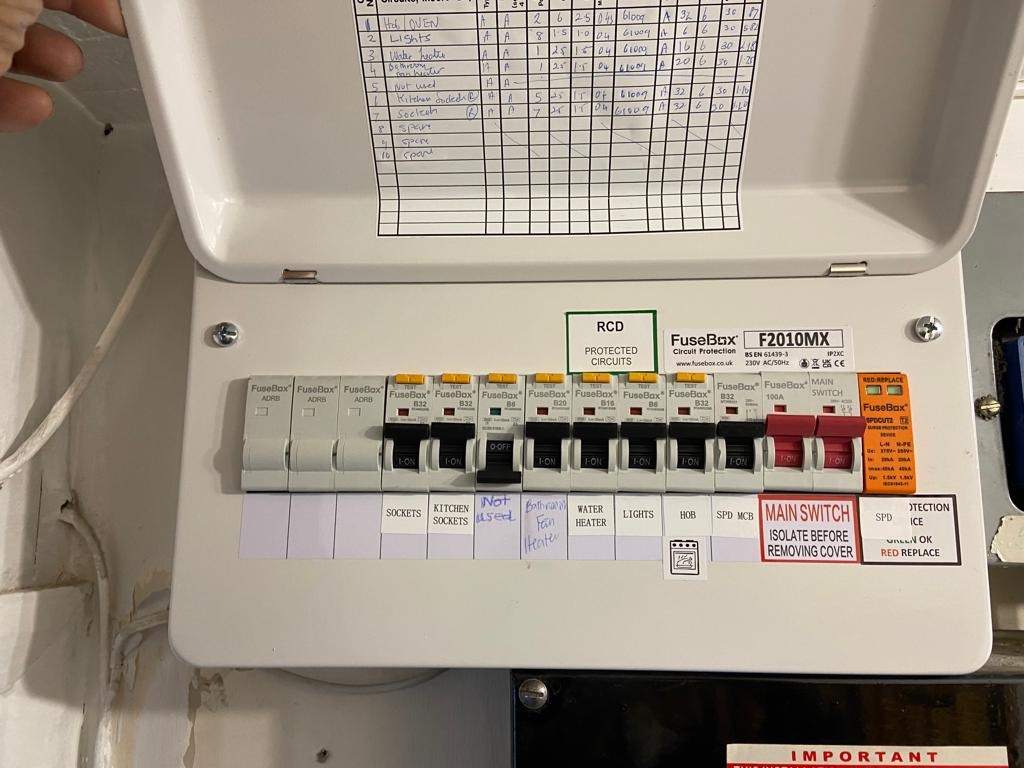
During an Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR certificate here) service in London, Circuit RCD (Residual Current Device) Testing is a crucial component of the assessment process to evaluate the effectiveness and performance of RCDs installed in the electrical circuits. Here’s how Circuit RCD Testing typically involves:
- Purpose: The purpose of Circuit RCD Testing is to verify the correct operation and responsiveness of Residual Current Devices (RCDs) installed in electrical circuits. RCDs are safety devices designed to quickly disconnect power in the event of an earth fault, reducing the risk of electric shock and fire hazards.
- Preparation: Before conducting Circuit RCD Testing, the electrician ensures that the electrical installation is disconnected from the power supply to prevent any risk of electric shock or damage to equipment. They may isolate individual circuits or sections of the installation to facilitate testing.
- Test Equipment: The electrician uses specialized RCD testers or instruments to perform Circuit RCD Testing. These testers apply test currents and simulate earth faults to assess the response time and sensitivity of RCDs installed in the electrical circuits.
- Testing Procedure: The electrician conducts RCD Testing on each circuit equipped with an RCD within the electrical installation. They apply test currents at various levels to trigger the RCD’s tripping mechanism and measure the response time and sensitivity of the device.
- Interpretation of Results: Based on the test results obtained during Circuit RCD Testing, the electrician interprets the findings to assess the performance and effectiveness of RCDs installed in the electrical circuits. They look for indications of proper tripping and resetting of RCDs within the specified response time and sensitivity thresholds.
- Comparison with Standards: The test results are compared to relevant industry standards, such as those outlined in the Wiring Regulations (BS 7671). These standards specify the acceptable response time and sensitivity requirements for RCDs based on factors such as circuit type, rating, and application.
- Documentation: The Circuit RCD Testing results are documented in the EICR report, along with any observations, defects, or recommendations related to RCD performance. The report provides a comprehensive overview of the condition and effectiveness of RCDs installed in the electrical installation and any actions required to address identified issues.
Overall, Circuit RCD Testing is a critical part of the EICR process, providing valuable insights into the performance and effectiveness of RCDs in protecting against electric shock and fire hazards. By conducting thorough testing and analysis, electricians can ensure that RCDs are functioning correctly and provide the necessary safety protection within the electrical installation.
How Do EICR Electricians Conduct Functional Checks of Electrical Components?
During an Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR) service, electricians conduct functional checks of electrical components and systems to assess their performance, functionality, and compliance with regulations. Here’s how EICR electricians typically conduct functional checks:
- Visual Inspection: Electricians begin by visually inspecting electrical components, systems, and equipment to identify any visible signs of damage, deterioration, or defects. They check for loose connections, damaged cables, overheating, corrosion, and other abnormalities that may affect functionality or safety.
- Switching Operations: Electricians perform switching operations to verify the functionality of switches, sockets, circuit breakers, and other control devices. They test the operation of switches to ensure they turn electrical circuits on and off properly, and they verify the functionality of sockets to ensure they provide power when connected to electrical appliances.
- Load Testing: Electricians conduct load testing on electrical circuits to assess their capacity and performance under normal operating conditions. They connect electrical loads, such as lamps, heaters, or appliances, to verify that circuits can handle the required electrical load without tripping circuit breakers or causing voltage fluctuations.
- Earth Fault Loop Impedance Testing: Electricians perform earth fault loop impedance testing to measure the impedance of the earthing system and verify its ability to safely clear earth faults. They apply test currents to simulate earth faults and measure the impedance of the earthing system to ensure it meets regulatory requirements and provides effective fault protection.
- RCD Testing: Electricians test Residual Current Devices (RCDs) to verify their proper operation in detecting earth faults and disconnecting power to prevent electric shock. They apply test currents to trigger the RCD’s tripping mechanism and measure the response time and sensitivity of the device to ensure it meets regulatory standards.
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Electricians perform insulation resistance testing to measure the resistance of insulation between conductors and verify its integrity. They apply test voltages and measure insulation resistance values to ensure they meet regulatory requirements and provide adequate protection against electric shock and short circuits.
- Functional Testing of Emergency Lighting and Fire Alarms: If applicable, electricians conduct functional testing of emergency lighting systems and fire alarm systems to ensure they operate properly during emergency situations. They activate emergency lighting units and test fire alarm sensors, sounders, and control panels to verify their functionality and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Documentation: Throughout the functional checks, electricians document their observations, test results, and any defects or abnormalities identified during the assessment. They compile this information into the EICR report, along with recommendations for remedial actions to address any issues and ensure the safety and compliance of the electrical installation.
By conducting thorough functional checks of electrical components and systems, EICR electricians can identify any defects, hazards, or non-compliance issues and recommend appropriate remedial actions to ensure the integrity, functionality, and safety of the electrical installation.